T568A vs T568B | Choosing the Right Ethernet Cable Wiring Standard
Ethernet cables are the backbone of wired network infrastructure, carrying data between computers, routers, switches, and other connected devices. When terminating twisted-pair copper cables for Ethernet, two wiring standards exist: T568A and T568B.
T568A and T568B are Ethernet cable color-coding standards with the only difference being the position of orange and green wire pairs; T568B is more common for new networks while T568A offers backward compatibility.
Understanding the key differences between these standards is crucial for anyone working with network cabling to avoid connectivity issues down the line. This article will explain T568A and T568B terminations in detail to help you choose the right scheme for your needs.

What Are T568A and T568B?
T568A and T568B are color-coding standards that define the specific pinout arrangements used when terminating twisted-pair Ethernet cables to 8P8C (RJ45) connectors. They are defined as part of the TIA/EIA-568 cabling standard published by the Telecommunications Industry Association (TIA).
The T568A and T568B standards ensure compatibility between cabling vendors and equipment manufacturers. They provide a consistent wiring framework to guarantee proper network performance.
Key Differences Between T568A and T568B
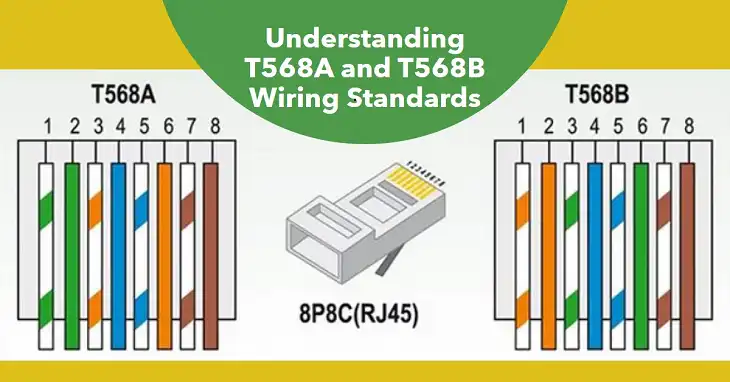
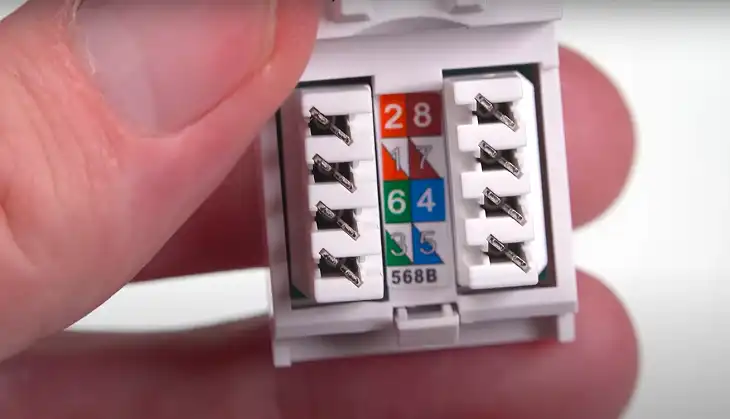
While T568A and T568B are functionally identical, they differ in the positioning of the orange and green wire pairs:
- T568A: Green, Orange, Blue, Brown
- T568B: Orange, Green, Blue, Brown
This table illustrates the color arrangements:
| Pin | T568A | T568B |
| 1 | White/Green | White/Orange |
| 2 | Green | Orange |
| 3 | White/Orange | White/Green |
| 4 | Blue | Blue |
| 5 | White/Blue | White/Blue |
| 6 | Orange | Green |
| 7 | White/Brown | White/Brown |
| 8 | Brown | Brown |
Apart from the swapped orange and green pairs, the wiring standards are identical. The remaining blue and brown pairs are in the same position for both.
Network Compatibility
When used consistently end-to-end, T568A and T568B work equally well for Ethernet networks up to 1000Base-T (Gigabit Ethernet). You can interconnect cables wired to T568A and T568B by using straight-through patch cables.
For connecting two identical devices directly without a switch, you need to use crossover cables with T568A on one end and T568B on the other. The transmit (TX) and receive (RX) pairs crossover to establish a valid link.
All modern Ethernet equipment features Auto-MDIX capability to automatically adjust for straight-through or crossover cables. However, crossover cables may still be required in some cases for older technology or troubleshooting purposes.
Transmission Speeds
The transmission speed supported by T568A or T568B depends on the overall cable category:
- Category 5: Up to 100 Mbps (Fast Ethernet)
- Category 5e: Up to 1 Gbps (Gigabit Ethernet)
- Category 6/6A: Up to 10 Gbps
Higher-rated cables like Cat5e and Cat6 are recommended for optimal performance with T568A/B, especially in new network installations.
Backward Compatibility
A key benefit of the T568A standard is backward compatibility with one and two-pair USOC wiring used for telephone and analog communications.
T568B does not offer the same level of compatibility with legacy cabling. However, it does match the older AT&T 258A standard.
Usage in New Networks
For new network installations, T568B is generally preferred and more widely adopted over T568A, except in cases that require backward compatibility.
The T568B standard has a simpler wire sequence that is easier for technicians to memorize and implement consistently. It also provides better noise immunity performance thanks to the way the wire pairs are arranged.
Advantages & Disadvantages
T568A
| Advantage | Disadvantage |
| Backward compatibility with telephone cabling | Less common in modern networks |
| Slightly less crosstalk | More difficult pinout to memorize |
T568B
| Advantage | Disadvantage |
| More widely used in Ethernet networks | Not compatible with older telephone wiring |
| Simpler pinout for termination | |
| Better noise immunity through wire pair twists |
How To Identify Existing Cables
When dealing with existing Ethernet cabling, you may not know if it is wired to T568A or T568B. There are a few ways to identify mystery cables:
To determine if an existing Ethernet cable is wired to T568A or T568B:
- Use a cable tester or wire tracer that can detect cabling pinouts. Connect the cable to the tester and it will analyze the wiring order to reveal if it is T568A or T568B.
- If you can access the RJ45 connector, visually inspect the wire colors starting from pins 1 and 2. If the first wires are orange/white-orange, it is T568B. If they are green/white-green, it is T568A.
- Check if the cable has any labeling on the jacket or at termination points indicating T568A or T568B wiring. This information may be printed directly on the cable.
- As a last resort if no other options are available, carefully open the RJ45 connector and visually trace the wire colors to determine if they match T568A or T568B sequence.
The best approach is to use a cable tester if available. Visually inspecting the connector or labels can also reliably identify the wiring type. Proper cable identification avoids mismatch issues when integrating cabling into networks.
How to Choose Between T568A and T568B
When choosing between wiring standards for a new installation, T568B is typically preferred unless you have a specific compatibility requirement. Reasons you may need to use T568A include:
- You need to integrate with older legacy systems that rely on T568A wiring:
- Some phone systems and building wiring installations from the 1980s/90s used T568A and may require this for compatibility.
- Your network devices only work with T568A
- Your organization has standardized on T568A for all installs
- Rare cases where industry regulations for your building/network require T568A – check your local codes.
If none of these factors apply, default to using T568B for new cable runs. It’s simpler to work with and more universally compatible with modern equipment.
Final Thoughts
T568A and T568B represent two viable standards for terminating Ethernet network cables. The choice depends on compatibility requirements, industry preferences, and existing infrastructure.
While T568B is more widely adopted in modern networks, T568A still has advantages for integrating with legacy cabling in older buildings and facilities. As long as you maintain consistency with one standard, both T568A and T568B can deliver reliable network connectivity.
FAQs
Which standard should I use for home networking?
For home networks, either T568A or T568B will work fine. Since T568B is more common, using it will make your installation more compatible if you ever need to integrate with other Ethernet cabling.
Can I use a cable with T568A on one end and T568B on the other?
This is not advisable. Using a crossover cable with mismatched ends often causes connection problems. Use T568A or T568B consistently end-to-end.
Why are guide tabs cut off on some RJ45 connectors?
The plastic guide tabs are sometimes clipped off to make plugging cables into dense switch ports easier. This does not impact connectivity as long as the wires are terminated correctly.
What cable tester should I use to verify the wiring order?
Cable testers from brands like Fluke Networks, Klein Tools, and Platinum Tools can identify cable pinouts and wiring faults. Consider investing in a high-quality cable tester if you work with networks professionally.