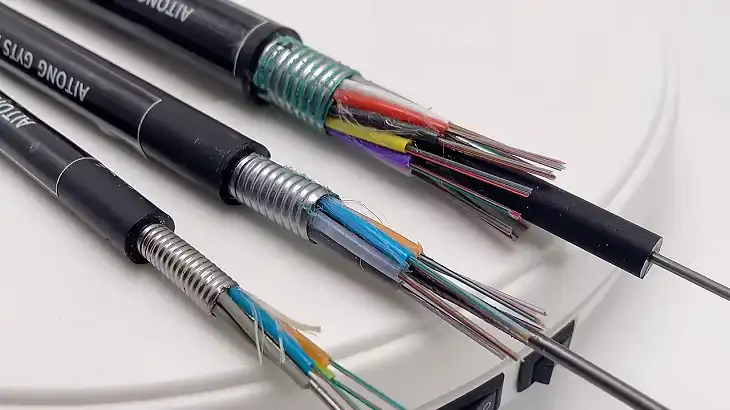
SM Fiber vs MM Fiber | Which should You Choose?
Fiber optic cables have transformed the way data is transmitted over long distances, enabling high-speed internet, smooth video streaming, and efficient communication in a range of industries. Single-mode (SM) and multi-mode (MM) fiber optic cables are the two primary types used in data communication networks.
While both transmit data using light pulses, they differ significantly in their core size, bandwidth capacity, and transmission distance. Here’s a breakdown of what makes each type unique, how they’re used, and which might be the better option for different applications.
What is Single-Mode Fiber?
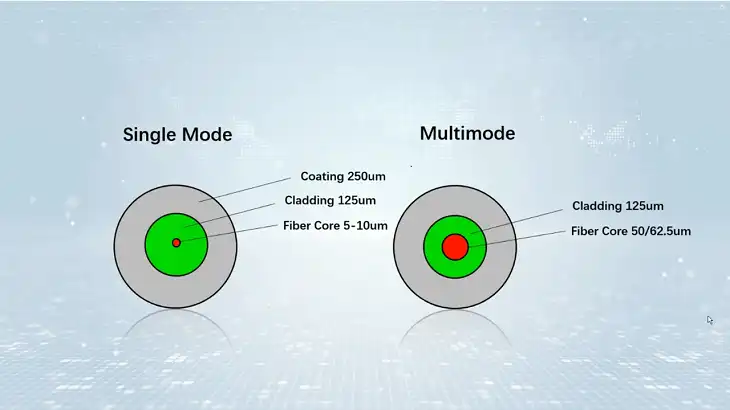
Single-mode fiber (SM fiber) is a type of optical fiber designed to carry light signals over long distances with minimal signal loss. It features a small core diameter, typically around 8-10 microns, which allows only one mode of light to propagate.
This single-path approach limits reflections within the fiber, reducing distortion and allowing the signal to travel far more efficiently than multi-mode fiber. The laser light source used in SM fiber enables high-capacity, long-distance data transmission with minimal interference, making it a strong choice for large-scale or high-speed networks.
Where is Single-Mode Fiber Used?
Due to its long-range capabilities and high data capacity, single-mode fiber is widely used in environments where data needs to travel over considerable distances without degrading. Key applications include:
Telecommunications Networks: Single-mode fiber is commonly used for connecting distant network hubs in city-to-city and even country-to-country telecommunications.
Internet Service Providers (ISPs): For data transmission between central offices and to connect to long-haul infrastructure, ISPs often rely on single-mode fiber to ensure reliable, high-speed internet access.
Data Centers: As data centers increasingly expand across large geographic areas, single-mode fiber is preferred for interconnecting various facilities over long distances.
Enterprise and Government Networks: Single-mode fiber is also used by corporations and government institutions with sprawling campuses or office locations that require high-speed data transfers over long distances.
What is Multi-Mode Fiber?
Multi-mode fiber (MM fiber) has a larger core diameter, generally ranging from 50 to 62.5 microns. This larger core allows multiple modes, or pathways, of light to propagate through the cable simultaneously.
The use of multiple paths enables multi-mode fiber to carry a high volume of data but can result in increased signal dispersion over longer distances, which slightly limits the range compared to single-mode fiber.
Multi-mode fiber typically uses light-emitting diodes (LEDs) as a light source, which are generally less expensive than the lasers used in single-mode fiber.
Where is Multi-Mode Fiber Used?
Multi-mode fiber is optimal for shorter-range applications where cost-effectiveness and high data transfer speeds are required over shorter distances. Common use cases include:
Local Area Networks (LANs): MM fiber is widely used in LAN environments such as in-office networks, university campuses, and hospitals where the distances between network points are limited.

Data Centers: For shorter interconnections within data centers, multi-mode fiber is an affordable solution, especially for high-density applications.
Audio/Visual and Video Applications: Multi-mode fiber is suitable for video applications like security camera networks, video streaming, and broadcasting where signals don’t need to travel over extensive distances.
What is the Difference Between SM and MM Fiber?
Single-mode and multi-mode fibers are designed for different applications, largely due to their structural differences, performance characteristics, and costs. Here’s a closer look at the key distinctions:
| Feature | Single-Mode Fiber (SM) | Multi-Mode Fiber (MM) |
| Core Diameter | 8-10 microns | 50-62.5 microns |
| Light Source | Laser | LED |
| Distance Capability | Up to 80 km or more | Typically up to 2 km |
| Data Transmission | Lower signal dispersion, suitable for long distances | Higher signal dispersion, optimal for short distances |
| Cost | Higher initial cost but efficient for long-term use | Lower cost, especially for short-distance needs |
| Bandwidth | High bandwidth capacity, supports high data rates over long distances | Lower bandwidth compared to single-mode, suitable for shorter connections |
These distinctions mean that while single-mode fiber is better for long-distance and high-bandwidth applications, multi-mode fiber offers a more cost-effective solution for short-range needs.
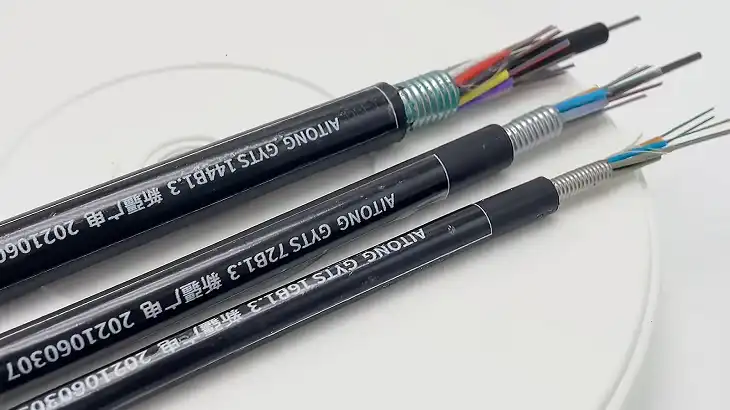

Single Mode vs Multi-Mode Fiber: Which is Better?
Deciding between single-mode and multi-mode fiber ultimately depends on the specific requirements of the network and the intended application. Single-mode fiber is considered better for:
- Long-Distance Requirements: If the network setup demands long-distance communication (up to 80 kilometers or more), single-mode fiber is the better choice.
- High-Speed Data Transmission: For applications requiring extremely high data rates, such as streaming massive data files or supporting high-capacity network infrastructure, single-mode fiber offers the best performance.
- Future-Proofing: Given its capability to support higher bandwidths, single-mode fiber can be advantageous for networks that anticipate expansion in data demand.
On the other hand, multi-mode fiber is often the better choice for:
- Cost-Sensitive, Short-Distance Projects: If the network setup is within a limited range (up to 2 kilometers), multi-mode fiber provides a cost-effective solution with sufficient data speed.
- High-Density Environments: For shorter links within data centers, LANs, or university campuses, multi-mode fiber can deliver excellent performance without the need for the higher cost of single-mode infrastructure.
Frequently Asked Questions
Can you convert mm to SM fiber?
Converting multi-mode to single-mode fiber is possible using media converters, but it can add latency and isn’t ideal for high-speed applications. It’s generally best to avoid conversion unless absolutely necessary, as it can degrade network performance.
What is the maximum speed of SM fiber?
Single-mode fiber can support incredibly high data transmission speeds. Speeds can reach up to 100 Gbps or even higher in some advanced configurations, and certain setups have achieved rates of 400 Gbps over long distances, with ongoing advancements pushing these limits even further.
Conclusion
The distinctions between SM and MM fibers are actually required for optimizing network performance and future-proofing your infrastructure. While MM fibers offer cost-effective solutions for short-distance, lower-bandwidth applications, SM fibers excel in long-haul, high-bandwidth scenarios. So, choose wisely.